How To Construct A Unit Circle?
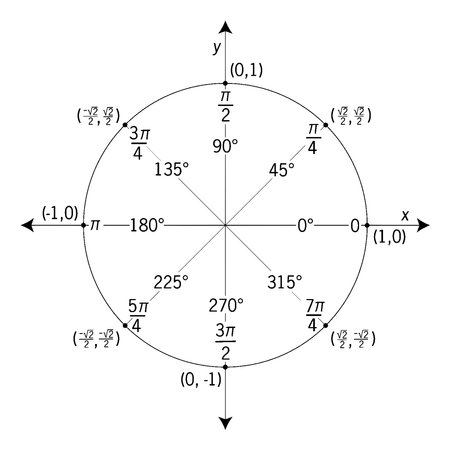
Constructing a unit circle involves several key steps. Start by drawing a circle with a radius of one unit. Label the center as the origin (0,0). Mark the four quadrantal points on the circle, corresponding to (1,0), (0,1), (-1,0), and (0,-1).
Divide the circle into 360 degrees or 2π radians, and mark the major angles, such as 30°, 45°, 60°, and their equivalent radians. To find coordinates for other points, use the trigonometric ratios sine and cosine.
For example, the coordinates for a point at 60° would be (1/2, √3/2). Accurate measurement and attention to detail are crucial. Constructing a unit circle visually represents angles and facilitates understanding of trigonometric concepts, making it a fundamental tool in mathematics.
Table of Contents
How Do I Construct A Unit Circle And Label Its Key Components?
Constructing a unit circle involves drawing a circle with a radius of one unit, designating its center as the origin (0,0). Label the four quadrantal points at (1,0), (0,1), (-1,0), and (0,-1). Divide the circle into 360 degrees or 2π radians, marking significant angles such as 30°, 45°, 60°, and their corresponding radians.
To label key components, understand the coordinates of points using trigonometric ratios like sine and cosine. For example, the coordinates for 60° are (1/2, √3/2). Additionally, a table of unit circle can be created, listing the major angles and their corresponding coordinates to serve as a quick reference.
This table aids in visualizing the relationships between angles and coordinates on the unit circle, enhancing comprehension of trigonometric principles.
Can You Provide Step-By-Step Instructions For Drawing A Unit Circle?
To draw a unit circle, start by designating the center as the origin (0,0) and drawing a circle with a radius of one unit. Mark the four quadrantal points at (1,0), (0,1), (-1,0), and (0,-1). Divide the circle into 360 degrees or 2π radians and mark significant angles like 30°, 45°, and 60° along with their corresponding radians.
Utilize trigonometric ratios, such as sine and cosine, to determine coordinates for other points. Ensure precision in measurement and attention to detail. A step-by-step approach involves understanding the key angles, dividing the circle accurately, and calculating coordinates systematically.
Consider creating a table of the unit circle, listing major angles and their coordinates for quick reference. This step-by-step process enhances visual representation and comprehension of trigonometric concepts associated with the unit circle.
What Are The Main Angles To Include When Constructing A Unit Circle?
When constructing a unit circle, it’s crucial to include key angles that provide a comprehensive understanding of trigonometric concepts. These main angles are typically 0°, 30°, 45°, 60°, and 90°, representing the first quadrant.
In radians, these correspond to 0, π/6, π/4, π/3, and π/2, respectively. Including these angles establishes a foundational framework for the unit circle, enabling a clear visualization of the relationships between angles and coordinates.
These angles serve as reference points for understanding trigonometric functions such as sine, cosine, and tangent, making them essential components in constructing a unit circle and fostering a deeper grasp of trigonometry.
How Does One Determine The Coordinates Of Points On A Unit Circle?
Determining the coordinates of points on a unit circle involves using trigonometric ratios. The basic trigonometric functions—sine and cosine—play a key role. For a given angle θ, the coordinates (x, y) on the unit circle are determined by x = cos(θ) and y = sin(θ).
The cosine of an angle gives the x-coordinate, representing the horizontal distance from the origin, while the sine provides the y-coordinate, indicating the vertical distance. As an example, for an angle of 60 degrees, the coordinates on the unit circle would be (1/2, √3/2), derived from cos(60°) and sin(60°).
This systematic approach allows for the precise determination of coordinates for any angle on the unit circle, facilitating a deeper understanding of trigonometric principles.
Are There Specific Tools Or Materials Recommended For Accurately Constructing A Unit Circle?
Constructing a unit circle requires minimal tools and materials. A compass is essential for drawing a circle with a precise radius of one unit. A ruler or straightedge aids in drawing diameters and dividing the circle accurately. Graph paper can provide a structured grid for additional precision.
If working with angles in radians, a protractor is useful for measuring and marking specific angles. While these tools are helpful, accuracy primarily depends on careful measurements and attention to detail. Overall, the construction of a unit circle is a straightforward process that can be achieved with basic geometric tools, making it accessible for both educational and practical applications.
What Is The Significance Of Radians When Constructing A Unit Circle?
Radians are crucial when constructing a unit circle as they provide a standardized measure for angles. Unlike degrees, which divide a circle into 360 parts, radians use the radius of the circle as the unit, measuring angles based on the arc length along the circumference.
In constructing a unit circle, angles measured in radians help establish a direct correlation between the angle’s measurement and the length of the arc on the unit circle. This makes calculations and coordinate determinations more straightforward, facilitating a clearer understanding of the trigonometric functions associated with the unit circle.
Radians simplify the representation of angles in mathematical contexts, particularly in calculus and advanced trigonometry, making them an essential concept when working with unit circles and trigonometric principles.





No Comment